Preparing for Total Knee Replacement: What to Do Before Surgery
Learn how prehab, strength training, and smart preparation before total knee replacement surgery can improve recovery and reduce stiffness.
If you’re scheduled for a total knee replacement (TKR), you’re probably feeling a mix of excitement, nerves, and maybe a little “what did I just sign up for?” 😅

Here’s the good news:
What you do before knee replacement surgery can significantly improve your recovery.
With the right preparation, many people experience:
- Faster healing
- Better knee motion
- Improved strength
- More confidence walking and using stairs
Think of it as training for the comeback.
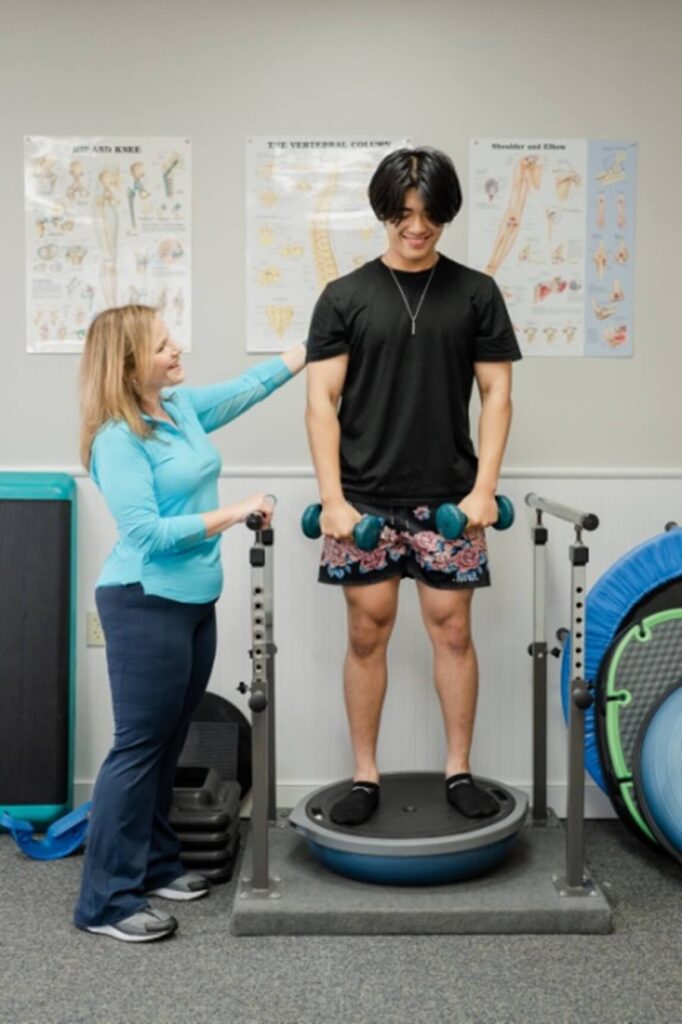
Why Prehab Before Total Knee Replacement Matters
Prehab (physical therapy before surgery) helps your body prepare for the demands of recovery.
Strong muscles and good movement going into surgery often lead to:
- Better post-op mobility
- Easier rehab
- Less stiffness
- More independence early on
In simple terms:
Stronger in = stronger out.
Key Goals Before Knee Replacement Surgery
1. Build Lower Body Strength
Your quadriceps, glutes, and hips play a huge role in:
- Standing up from chairs
- Walking safely
- Protecting your new knee
Simple exercises like sit-to-stands, step-ups, and leg raises can make a big difference.
2. Improve Knee Range of Motion
You don’t need perfect movement before surgery, but gentle bending and straightening helps:
- Reduce stiffness
- Make post-op exercises easier
- Improve confidence
3. Practice Functional Movements
Before surgery, it’s helpful to rehearse:
- Getting in and out of chairs
- Using stairs
- Walking with an assistive device
Consider it a “practice run” for your new knee.
How to Prepare Your Home for Recovery
A little planning now saves stress later.
Helpful tips:
- Raise toilet and chair height
- Remove loose rugs
- Keep essentials at waist level
- Set up a comfortable recovery area
- Have ice packs and pillows ready
Bonus points for a stocked fridge and a solid Netflix lineup. 🎬
What NOT to Worry About
You don’t need to:
- Be in perfect shape
- Have zero pain
- Know every exercise
You do need:
- Consistency
- Guidance
- A positive mindset
Progress beats perfection every time.
Your Mindset Affects Your Recovery
Feeling informed and prepared reduces anxiety and improves outcomes.
Confidence + consistency = better recovery.
Final Thoughts on Preparing for Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is a journey — and it starts before surgery.
With proper preparation, strength training, and guidance, you can walk into surgery feeling confident and walk out stronger than you expect.
Your future knee will thank you. 🦵✨
FAQ: Preparing for Total Knee Replacement
How long should I do prehab before knee replacement surgery?
Ideally, 3–6 weeks of prehab can make a big difference. Even a short period of focused strengthening and mobility work can improve your recovery and confidence after surgery.
Can prehab reduce pain after surgery?
Prehab won’t eliminate all post-op pain (this is surgery, after all), but it can help your body handle rehab better, improve movement sooner, and reduce stiffness.
Do I still need physical therapy if I’m already active?
Yes! Being active is great, but targeted strength, mobility, and movement training helps protect your new knee and speeds up recovery — especially for stairs, walking, and daily activities.
What’s the most important thing to focus on before surgery?
Strength, safe movement, and mindset. Strong muscles + realistic expectations = smoother recovery.
Can I do prehab virtually?
Absolutely. Virtual PT is a great option if you want expert guidance from home while still getting a personalized plan.
Ready to Feel Confident About Your Knee Surgery?
Whether you’re preparing for a total knee replacement or already scheduled for surgery, the right plan can make your recovery smoother, stronger, and less stressful.
I offer customized prehab and post-op rehab programs — both in-person and virtually — so you can move forward with confidence.
Your new knee deserves a smart game plan.
Let’s build it together. 🦵💪